Diabetes has become a very prevalent medical condition in the last decade. Many say it is due to the change in the daily lifestyle, which has negatively impacted our dietary patterns and level of physical activity. Let’s take a look at what’s happening locally, get advice from our dietician and then learn to manage your diabetes and live a happy, fulfilled life.
Diabetes in Zambia
In 2016, a sample population of 45,767 Zambians found that 3.5% were Diabetic, and 34.5% were unaware of their diagnosis. Of the individuals diagnosed with diabetes, 66% of those Zambians were not on any treatment, and 34% had a blood glucose level beyond the recommended levels of > 7.8 mmol. That’s a lot of people without the necessary information they might need to live safely with diabetes.
Management of Diabetes
Unfortunately, a vast majority believe having diabetes can be managed by limiting or eliminating sugars. However, the management of the disease is more than that. Several nutrients influence the health of an individual with diabetes. However, even though people with diabetes must observe several nutrients, nutritional management of diabetes is not complex.
Where do carbohydrates fit in?
Carbohydrates are a critical nutrient for individuals diagnosed with diabetes. There are two types of carbs, which are complex and simple and have varying effects on your blood sugar.
A complex carb (whole grains, legumes, vegetables) is made of sugar molecules that take time to break down to provide energy. Thus having a blunt impact on blood sugar.
Simple carbs are individuals’ sugars and are broken down rapidly to give energy and tend to cause a spike in blood sugar (processed foods, candy, sugary beverages).
Complex carbs are also high in fibre, which is the slowest to digest. Therefore this is critical in keeping blood sugars under control. People with diabetes must understand that if you have this condition, you don’t have to eliminate carbs but be wise and opt for high-fibre carbs. Additionally, avoid eating large portions at one time rather than eating smaller and more frequent meals throughout the day.
What about fats?
The next critical nutrient to monitor is the consumption of fats. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of heart disease, so they must follow a heart-healthy diet. A heart-healthy diet tends to focus more on unsaturated fats such as nuts, seeds, and seafood and limit foods rich in saturated fats such as proceeds food and red meat products.
Additionally, fibre-rich foods assist in controlling blood sugar and help manage cholesterol levels, therefore, heart healthy and help manage diabetes. Decreased sodium consumption is also essential in maintaining blood pressure and aids heart health. It is important to limit sodium consumption to 2300 milligrams grams per day which is equivalent to1 a teaspoon a day.
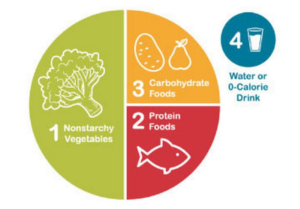
People with diabetes need to follow four basic rules when it comes to meals;
- Aim to fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables (spinach, asparagus, green beans, bean sprouts, peppers, carrots, eggplants, mushrooms etc.). The more significant section is allotted to foods low in carbs. Still, it has copious amounts of vitamins, minerals and fibre, which is a critical part of the diet.
- A quarter of the plate should be carbohydrates such as brown bread, brown rice, whole wheat pasta or starch vegetables such as corn, potatoes, peas and pumpkin; Dairy foods such as milk, yoghurt, cheese, sour milk, soy milk etc. and fruits (fresh, juiced or dried).
- The remaining quarter of the plate must be lean animal or plant-based proteins. There is an emphasis on eating lean meats as these are heart-healthy.
Animal-based include;
- fish
- seafood
- chicken
- turkey
- lean cuts of beef or pork
- eggs,
- low-fat cheese and cottage cheese.
Plant-based proteins include;
- soy
- lentils
- quinoa
- chia seeds
- hemp seeds
- tempeh
- beans
- nut butter
4. Hydrate by consuming low-calorie drinks, such as water, unsweetened tea, coffee, or fresh fruit juice.
Integrative Nutrition & Managing Diabetes
While paying attention to what you eat if you have diabetes is essential, it is also important to consider ways to live life to the fullest. The Institute of Integrative Nutrition encourages people to look at what nourishes a person beyond the actual food on the plate. One must consider what satisfies them, such as relationships, physical activity, career, and spirituality. These lifestyle factors are considered to be a person’s primary food, while the food on your plate, is considered secondary food.
Three Lifestyle Habits to practice daily if you have a Diabetes Diagnosis
-
Meal planning and timing
Preparing your meals ahead of time can help you better manage your lifestyle with diabetes. Consider how to fit having balanced meals & snacks into your already hectic daily life. Planning is key. Consider sitting down every weekend to plan your meals for the week ahead. Make time to batch cook. Double the recipe and freeze the other half, ensuring you have healthy options for weeks when life gets too busy to focus on food. Don’t be afraid to ask for help. Meal planning and prepping when you have diabetes can be tricky, but the payoff can be significant.
-
Physical Activity
Regular exercise is an important lifestyle habit to have while managing diabetes. Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity for people with diabetes during and after exercise. For those with type 1 diabetes, exercise can help the insulin from your medication be more bio-available to your body. Physical activity may help bump up the production of your brain’s feel-good neurotransmitters, called endorphins. Although this function is often referred to as a runner’s high, aerobic activity, such as a game of tennis or a nature hike, can contribute to this feeling. As per the CDC, the recommended goal is to get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week. Before starting an exercise program make sure to check-in with your physician.
-
Emotional Health and Stress
Stress can increase your heart rate and cause the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline that spike blood sugar levels. Research also suggests that stress is a lifestyle factor contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes, as stress hormones inhibit insulin-producing cells in the pancreas from working correctly. As you probably know, stress can cause a person to reach for unhealthy food options, such as comfort food that might be higher in sugar. You must be aware of how stress can sabotage your insulin and have a plan regarding how to deal with stress. Stress management techniques include guided meditation, deep breathing, management of social media/news exposure and connection with others.
In a nutshell
A Diabetes diagnosis does not have to stop you from living your life to the fullest. The good news is that diet and lifestyle changes can go a long way in helping you to manage the disease. Your body is unique, and with time and energy, you can learn how your body responds to food and the environment you live in. Using meal planning, exercise and stress reduction is a great way to tune into what your body is telling you and help you live the life you want.